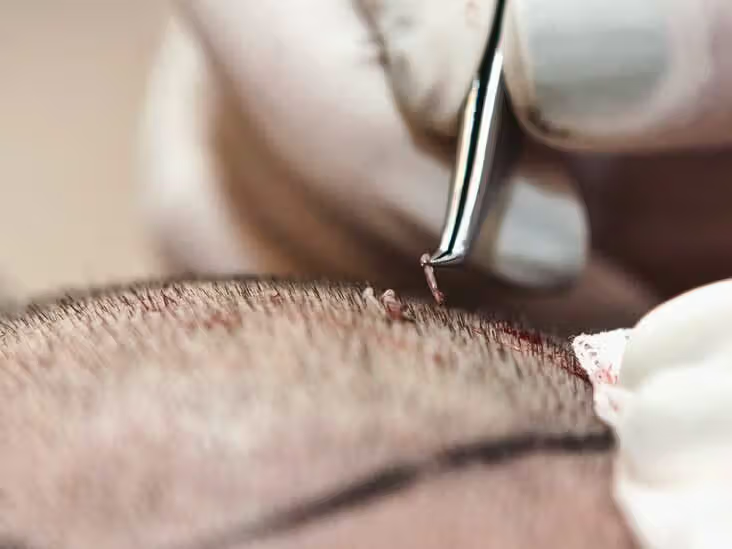
Hair transplant surgery is one of the most trusted and permanent solutions for baldness. With techniques like Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) and Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), millions of people achieve natural-looking results every year.
According to the International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS), more than 90% of patients experience only mild, temporary side effects after a hair transplant — most of which resolve on their own. Still, it’s important to remember that no surgery is completely free of risks.
In this blog, we’ll cover:
• Common short-term side effects after a hair transplant
• FUT vs FUE specific complications
• Short-term vs long-term risks (with a comparison table)
• Rare and psychological side effects patients should know about
• Tips to minimize risks and ensure smooth recovery
• Frequently asked questions (FAQs) answered by experts
Reading about side effects is important to set the right expectations. But remember — every patient heals differently. Always follow the instructions of your hair transplant surgeon for the best results and to minimize risks.
What is a Hair Transplant?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure in which healthy hair follicles are moved from a donor site (usually the back or sides of the scalp) to thinning or bald areas. It is the only permanent solution to restore natural hair growth.
The two most common techniques are:
• Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT): Also called the “strip method,” this involves removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, separating follicular units, and implanting them into the recipient area. FUT is effective for covering larger bald patches but leaves a linear scar. Recovery is slightly longer compared to FUE.
• Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE): This technique extracts individual hair follicles using tiny punches and implants them into bald areas. FUE leaves minimal scarring and offers faster healing, but requires precision and expertise to avoid overharvesting.
Both procedures are safe and widely practiced. However, since they differ in technique, their side effects and recovery experience also vary, which we’ll explore in the next sections.
👉 Read More: Hair Transplant in India
Common Side Effects After Hair Transplant
After a hair transplant, most patients experience a few short-term side effects. These are part of the natural healing process and generally resolve within days or weeks. With the right care, you can minimize discomfort and speed up recovery.
Swelling
Swelling is the most common side effect after hair transplant surgery. It usually develops on the forehead and sometimes around the eyes within 2–3 days. While it may look uncomfortable, it is harmless and typically disappears within a week.
How to manage/prevent: Sleep with your head elevated, apply cold compresses (not directly on grafts), and take anti-inflammatory medicines as prescribed.
Bleeding
Some minor bleeding is normal after the surgery. It occurs because of the tiny incisions made in the scalp for graft placement. In most cases, the bleeding stops on its own within the first 24 hours and is easily controlled with light pressure or dressings.
How to manage/prevent: Avoid scratching, rubbing, or bending the head too much. Follow your surgeon’s cleaning instructions carefully, and if bleeding continues, seek medical advice.
Infection
Infection is rare, especially when the procedure is performed in sterile conditions by an experienced surgeon. However, if the scalp is not kept clean or if you scratch the area, infection may occur. Signs include redness, swelling, or pus.
How to manage/prevent: Keep the scalp clean, avoid touching it with dirty hands, and complete the antibiotic course given by your doctor.
Shock Loss (Temporary Shedding)
It can be worrying when transplanted hair — and sometimes surrounding natural hair — starts falling out a few weeks after surgery. This phenomenon, known as shock loss, is temporary. It happens because the follicles enter a resting phase after transplantation. Regrowth usually begins within 3–4 months.
How to manage/prevent: Be patient — this is a natural stage. Follow a healthy diet, avoid stress, and use only the medicines or hair growth serums recommended by your surgeon.
Scabs and Itching
Tiny crusts or scabs often form around the implanted follicles within the first week. These may cause mild itching as the scalp heals. This is normal and temporary, clearing within 10–14 days.
How to manage/prevent: Do not pick or scratch scabs. Wash gently with a medicated shampoo as advised by your doctor. Moisturizing sprays prescribed post-surgery may also help.
Pain and Numbness
Since a hair transplant is a surgical procedure, mild pain or discomfort is expected for a few days. Some patients may also notice numbness or tingling in the donor or recipient areas. Pain usually improves with prescribed medication, while numbness may last a few weeks before fading naturally.
How to manage/prevent: Take pain relievers as prescribed and avoid strenuous activity for a few days. If numbness or pain persists for more than 2–3 months, consult your surgeon.
👉 Note: These side effects are temporary and generally mild. Most patients recover without complications if they carefully follow their surgeon’s aftercare instructions.
FUT-Specific Side Effects (Strip Surgery)
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) can cover large bald areas effectively, but it has some unique side effects:
• Linear Scar: A visible scar may remain at the donor site. Keeping hair longer usually hides it.
• Folliculitis: Small red bumps around follicles. Clears with antibiotics or warm compresses.
• Suture Issues: Non-dissolvable stitches may cause irritation but are managed in follow-ups.
• Keloid/Hypertrophic Scar: Thick raised scars may develop in scar-prone individuals.
• Donor Shock Loss: Temporary shedding of hair around the strip area; regrows in a few months.
• Necrosis (Rare): Tissue damage due to poor blood supply; very uncommon with expert care.
👉 Most FUT side effects are temporary or manageable with proper post-op care.
FUE-Specific Side Effects (Punch Extraction)
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE) leaves no linear scar, but it has its own potential side effects:
• Donor Site Depletion: Overharvesting may leave a patchy or “moth-eaten” look.
• Pinpoint Scarring: Tiny white dots (hypopigmentation) may appear at extraction sites.
• Buried Grafts/Ingrown Hair: Improper extraction can push follicles under the skin, forming small bumps.
• Overharvesting/Transection: Excessive extraction may thin the donor area permanently.
• Epithelial Cysts: Small lumps may form if grafts are not fully removed.
• Persistent Numbness/Pain: Tingling or numbness may last for weeks; usually fades over time.
• Necrosis (Rare): Very rare tissue damage due to poor healing.
👉 FUE is considered less invasive than FUT, but careful technique and skilled hands are essential to avoid complications.
Short-Term vs Long-Term Side Effects of Hair Transplant
Most side effects after a hair transplant are short-lived, but a few can extend over months or, in rare cases, become long-term. Knowing what to expect helps patients stay prepared and worry less during recovery.
| Timeline | Possible Side Effects | Severity | Recovery/Management |
| 1–7 days | Swelling, mild bleeding, scabs, itching, pain | Mild | Clears naturally with rest & medication |
| 2–4 weeks | Shock loss (temporary shedding), tenderness | Mild | Regrowth starts after 3–4 months |
| 3–6 months | Donor site thinning, numbness, occasional folliculitis | Moderate | Usually improves with medical care |
| 6+ months (rare) | Scarring, donor depletion, persistent numbness, necrosis | Rare | Needs expert medical evaluation |
👉 Key takeaway: Most side effects are temporary and manageable, while rare long-term risks are preventable if you choose a skilled surgeon and follow aftercare instructions.
Rare & Psychological Side Effects
In rare cases, patients may experience less common complications or psychological stress:
• Excessive Scarring: Keloids or hypertrophic scars in patients prone to abnormal healing.
• Donor Site Overharvesting: Excessive extraction can permanently thin the donor area.
• Permanent Numbness: Rare nerve damage may cause long-term tingling or loss of sensation.
• Necrosis: Very rare tissue death due to poor blood supply; requires urgent medical care.
• Anxiety & Stress: Worry about shock loss or delayed results is common. Counseling and realistic expectations help.
How to Minimize Hair Transplant Side Effects
Most side effects can be reduced or avoided with the right care. Here are some essential tips:
• Choose an experienced surgeon: The skill of your surgeon plays the biggest role in minimizing complications.
• Follow pre- and post-op instructions carefully: Every patient receives specific do’s and don’ts — stick to them strictly.
• Keep the scalp clean: Wash gently as advised, and avoid scratching or rubbing.
• Avoid smoking and alcohol: These slow down healing and increase the risk of infection.
• Protect from direct sun exposure: Wear a loose cap or stay indoors to prevent damage to healing grafts.
• Take prescribed medicines only: Painkillers, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs must be taken exactly as recommended.
• Sleep with head elevated (first few days): This helps reduce swelling.
• Avoid strenuous activities: Heavy workouts, swimming, and bending should be paused until your surgeon clears you.
• Attend follow-up appointments: Early detection of complications ensures quick treatment.
👉 Following these steps, along with your surgeon’s personalized advice, ensures a smoother recovery and healthier results.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Is a hair transplant safe?
Yes. Hair transplants are generally safe when done by qualified surgeons. Most side effects are mild and temporary, such as swelling or itching.
Q2. How long do side effects last after a hair transplant?
Most short-term side effects like swelling, pain, and scabs clear within 1–2 weeks. Temporary shedding (shock loss) lasts a few months before regrowth begins.
Q3. What is shock loss after a hair transplant?
Shock loss is temporary shedding of transplanted and nearby natural hair due to surgical stress. It usually happens within the first 2 months, and regrowth starts after 3–4 months.
Q4. Can a hair transplant cause permanent damage?
Permanent complications are rare but possible, such as scarring, donor area thinning, or persistent numbness. These risks are minimized when surgery is done by an expert.
Q5. Will I have visible scars after a hair transplant?
• FUT leaves a linear scar in the donor area.
• FUE leaves tiny dot-like scars that are less visible.
The visibility depends on technique, surgeon’s skill, and your healing process.
Q6. How painful is recovery after a hair transplant?
Mild pain or tightness is common for the first few days. This is usually well managed with prescribed painkillers.
Q7. What should I avoid after a hair transplant?
Avoid scratching, smoking, alcohol, swimming, heavy exercise, and direct sun exposure until cleared by your surgeon.
Q8. Can infection happen after a hair transplant?
Yes, but it is rare. Keeping the scalp clean, completing your antibiotic course, and avoiding touching the grafts help prevent infection.
Q9. How soon will I see results after surgery?
New hair usually starts growing 3–4 months after surgery, with full results visible after 9–12 months.
Q10. When should I contact my doctor about side effects?
Seek medical advice if you notice persistent bleeding, severe pain, pus, fever, or numbness that doesn’t improve over time.
References
- International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (ISHRS): http://www.ishrs.org
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD): http://www.aad.org
- PubMed: Hair transplant complications and safety studies: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Disclaimer
This article is for informational purposes only and should not replace medical advice. Always consult a qualified dermatologist or hair transplant surgeon before undergoing the procedure.



Leave a Reply